Oral Thrush is a common fungal infection that affects the inside of the mouth, typically caused by the overgrowth of Candida albicans. This condition, also referred to as oral yeast infection, often appears as creamy white spots on the tongue, cheeks, roof of the mouth, or throat. It can affect people of all ages but is especially common among infants, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
In this article, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, risk factors, prevention methods, and effective treatment options for oral thrush. If you’re experiencing discomfort or visible changes in your oral health, understanding this condition will help you take timely action.
The primary cause of oral thrush is an imbalance that leads to excessive growth of Candida, a yeast organism that normally lives harmlessly in the body. Although it is naturally present in the digestive system and mouth, certain triggers can cause it to grow beyond normal levels.
These factors disrupt the oral microbiome, allowing yeast to overpower the body’s natural defenses.
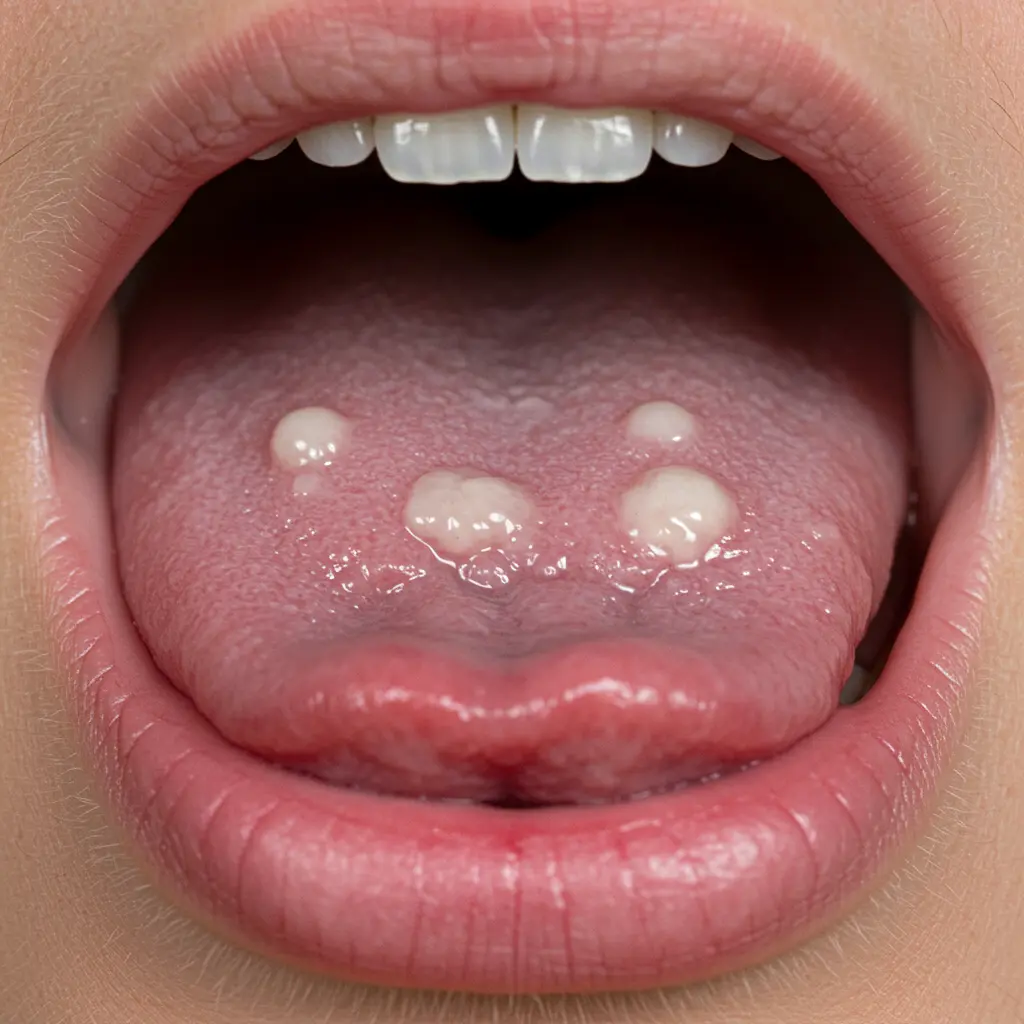
Spotting the signs of oral thrush early can make treatment more effective. The condition can be mild at first but may worsen without proper care.
Key Symptoms Include:
In severe cases, oral thrush may spread to the esophagus, causing more significant discomfort and complications
Although oral thrush can affect anyone, some people face a higher risk. Newborns and older adults, especially those who wear dentures, are more likely to experience it. Additionally, individuals undergoing chemotherapy or radiation therapy, or those taking medications like corticosteroids or immunosuppressants, are more vulnerable.
Even healthy adults may develop thrush if they maintain poor oral hygiene or follow a diet high in sugar and yeast-promoting foods.
Dentists or physicians typically diagnose oral thrush by visually examining the mouth and tongue. In most cases, no lab tests are needed. However, if the condition persists or spreads, a sample of the infected tissue may be sent for further testing to rule out underlying medical conditions.
It’s crucial not to ignore prolonged symptoms, as they may indicate a deeper immune or systemic issue requiring further attention.
Here’s the positive news: oral thrush can be effectively treated with proper and timely care. Depending on the severity and underlying cause, your dentist or doctor may recommend:
Antifungal Medications:
Home Care Tips:
With proper treatment, most people recover from oral thrush within a week or two.
Prevention is always better than cure, and a few lifestyle changes can significantly reduce your chances of developing oral thrush.
Simple Ways to Prevent Oral Thrush:
Practicing good oral hygiene is your best defense against oral infections and other complications.
Oral thrush is particularly common in babies, often appearing within the first few weeks after birth. It may cause fussiness or trouble feeding, but it usually clears up quickly with pediatric antifungal treatments.
In elderly patients, especially those with dry mouth or dentures, maintaining oral hygiene is critical. Caregivers should assist with cleaning routines and look out for signs of redness or white patches.
If you notice persistent white patches in your mouth or experience discomfort while eating or swallowing, it’s essential to consult a dentist. Early intervention not only prevents complications but also helps identify any underlying conditions that may require attention.
Oral thrush can be kept under control if diagnosed early and treated with the correct methods. With proper hygiene, dietary adjustments, and professional care, most cases resolve without complications. If you’re experiencing symptoms of oral thrush or any unusual changes in your oral health, don’t wait—get a professional evaluation.
Looking for expert dental care to treat oral thrush effectively? Choose Unidental for expert care and lasting comfort. Our skilled dental team is committed to your complete oral health journey. Our team of experienced dental professionals is here to support your oral health journey.
Oral thrush is not highly contagious. However, people with weakened immune systems may be more likely to develop it after close contact.
Mild cases may resolve without treatment, but most require antifungal medication for complete relief.
With proper treatment, oral thrush usually clears up within 7–14 days.
Stress reduces your immune defenses, which increases the risk of developing infections like oral thrush.
Hyderabad : +91 6305 971445
Anantapur: +91 70758 90089
Goa: +91 83266 32500
Mon to Sat 10:00AM to 8:00PM
Sun 10:00AM to 12:00PM

Our goal is to provide friendly, caring dentistry with the highest standards in general, cosmetic, and specialist treatments. We strive to be the best dental hospital for comprehensive oral care.
We use advanced dental technology to deliver safe, precise, and painless treatments for every patient.