Gingivitis is one of the most common and mild forms of gum disease that affects millions worldwide. Caused mainly by poor oral hygiene, gingivitis results in redness, swelling, and irritation of the gums. Although it may seem minor at first, if left untreated, gingivitis can lead to severe periodontal diseases and even tooth loss.
Understanding the early signs of gingivitis and how to manage or reverse it is crucial for maintaining long-term dental health. Let’s explore everything you need to know about this condition from its causes to prevention strategies and treatment options.
The primary cause of gingivitis is the buildup of plaque a soft, sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. When plaque isn’t cleared routinely with brushing and flossing, it turns into tartar, which can inflame the gums and trigger early symptoms of irritation.
Other risk factors include:
These factors can weaken your immune response, making it easier for bacteria to cause gum inflammation.
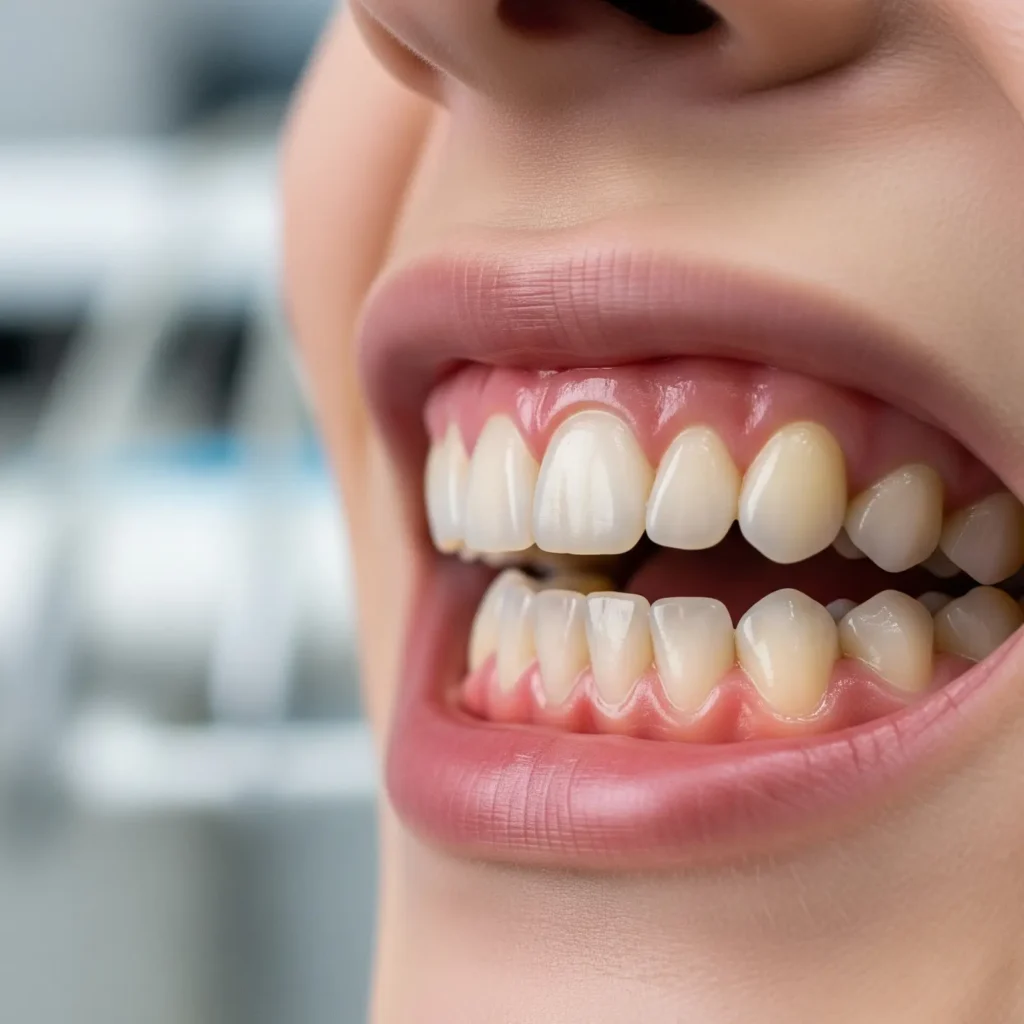
Gingivitis often develops silently, with symptoms being painless in the early stages. However, timely recognition of these signs can help in prompt treatment.
Common symptoms include:
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s best to consult a dentist before the condition worsens into periodontitis.
While gingivitis affects the gums, its implications go beyond the surface. Chronic gum inflammation can weaken the tissues and bones that support your teeth. In severe cases, it may lead to tooth mobility and eventual tooth loss.
Moreover, gum inflammation has been linked to other health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections. This connection is due to the inflammatory response triggered by oral bacteria entering the bloodstream.
Effective dental hygiene plays a pivotal role in preventing gingivitis. Brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily helps remove plaque before it hardens into tartar.
Consider using a soft-bristled toothbrush and an antibacterial mouthwash to further reduce plaque formation.Electric brushes often help clear plaque better from tricky spots, particularly for those who have difficulty with precise hand or wrist movement while brushing.
Regular dental visits are vital to prevent and manage gingivitis. Dentists can detect early gum inflammation even when you don’t feel any pain. Tartar deposits that brushing can’t remove are cleared away effectively with dental cleaning.
A typical dental cleaning, known as scaling and polishing, involves removing plaque from above and below the gumline. If tartar is extensive, a deep cleaning procedure called root planing may be recommended.
Your diet plays a vital role in maintaining gum health. A diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals helps strengthen the gums and boosts your immune response to oral bacteria.
Foods that support gum health include:
Foods to avoid:
Eating well, combined with good oral hygiene, dramatically lowers the risk of gum disease.
Although both conditions fall under the umbrella of gum disease, gingivitis and periodontitis are not the same.
Periodontitis is severe; gums and bone recede from teeth, creating spaces that trap bacteria and worsen the damage without timely dental intervention.
Without treatment, gingivitis can progress into periodontitis. Early intervention can prevent this escalation, which is why regular dental checkups and cleanings are so important.
When caught early, gingivitis can be reversed with a combination of professional care and improved personal hygiene.
Common treatment options include:
In addition to these, your dentist may recommend lifestyle changes like quitting smoking or managing underlying health conditions.
Gingivitis is preventable, treatable, and even reversible when caught early. Consistent oral hygiene practices, regular dental visits, a nutritious diet, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking are the most effective ways to keep your gums healthy.
If you notice red, swollen, or bleeding gums, don’t delay treatment. Addressing gingivitis at its earliest stage ensures long-term dental health and prevents complications down the road.
For expert diagnosis, treatment, and personalized gum care, schedule a consultation with Unidental, your trusted dental care provider.
Yes, gingivitis is reversible if treated early. Proper brushing, flossing, and regular dental cleanings can completely restore gum health.
With proper dental care, signs may lessen in just a few days to two weeks' time. However, treatment time varies depending on the severity of the condition.
While gingivitis itself isn’t contagious, the bacteria that cause it can be transmitted through saliva, making good hygiene important even among family members.
Yes, children and teenagers can also develop gingivitis, especially if they have poor oral hygiene or wear orthodontic appliances.
Not necessarily. Gingivitis often develops silently without pain. That’s why recognizing other signs like bleeding or swollen gums is crucial.
Hyderabad : +91 6305 971445
Anantapur: +91 70758 90089
Goa: +91 83266 32500
Mon to Sat 10:00AM to 8:00PM
Sun 10:00AM to 12:00PM

Our goal is to provide friendly, caring dentistry with the highest standards in general, cosmetic, and specialist treatments. We strive to be the best dental hospital for comprehensive oral care.
We use advanced dental technology to deliver safe, precise, and painless treatments for every patient.